Audio Identifier 0.7.1
Audio Identifier is serving as an audio inspector. It provides you instantly with information about your audio tracks.
This function comes in handy when you want to perform file conversion or prepare audio files for mobile devices.
The main features of Audio Identifier are the full Unicode support, the LAME tag info displaying, the interface supporting various skins, being able to work with lots of formats and to export data to HTML.
With Audio Identifier, you can find what are the average bitrate, the guessed quality and the user encoder for the following formats: MP3, MPC, WAV, VQF, OGG, WMA, AAC, SPX, APE, WV, FLAC, TTA, OFR, AC3 and DTS.
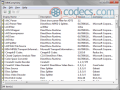
The interface is user-friendly and it has an Explorer-based layout. For each item you will know the name, format, length, size, encoder name, bit rate, encoding properties and quality.
Due to advanced options, you can find out if the audio track contains VI, ID3, ID3 V2 or APE tags.
The settings of this virtual item allow you to make Audio Identifier stay on top of other applications, automatically collapse the selected folder, getting back to default settings and integrating Audio Identifier into the Explorer context menu. You will also get an estimation of the quality by assessing bit rate.
Audio Identifier has not been updated since 2008, which should not be a problem as long as it does its job flawlessly and respond instantly to commands.
The application is stable and reliable, it has a small size and it uses a low to medium amount of system resources.
In conclusion, Audio Identifier is a utility tool worth deploying on your computer, when you work a lot with audio files and you are interested in their technical specifications.
The main features of Audio Identifier are the full Unicode support, the LAME tag info displaying, the interface supporting various skins, being able to work with lots of formats and to export data to HTML.
With Audio Identifier, you can find what are the average bitrate, the guessed quality and the user encoder for the following formats: MP3, MPC, WAV, VQF, OGG, WMA, AAC, SPX, APE, WV, FLAC, TTA, OFR, AC3 and DTS.
The interface is user-friendly and it has an Explorer-based layout. For each item you will know the name, format, length, size, encoder name, bit rate, encoding properties and quality.
Due to advanced options, you can find out if the audio track contains VI, ID3, ID3 V2 or APE tags.
The settings of this virtual item allow you to make Audio Identifier stay on top of other applications, automatically collapse the selected folder, getting back to default settings and integrating Audio Identifier into the Explorer context menu. You will also get an estimation of the quality by assessing bit rate.
Audio Identifier has not been updated since 2008, which should not be a problem as long as it does its job flawlessly and respond instantly to commands.
The application is stable and reliable, it has a small size and it uses a low to medium amount of system resources.
In conclusion, Audio Identifier is a utility tool worth deploying on your computer, when you work a lot with audio files and you are interested in their technical specifications.